Artificial nose (Swedish) - A cap that can be attached to a
tracheostomy tube to help maintain humidity.
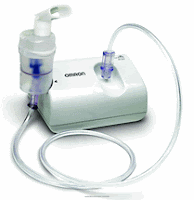
Air compressor -
A machine used to provide air or oxygen under pressure to make breathing easier
for a patient with breathing problems.
Apnea monitor - A
device used to check to make sure that a patient with a breathing tube
(endotracheal tube) or a tracheostomy tube hooked to a ventilator does not stop
breathing. It can sound alarm to alert care provider in case of slowed or
stopped breathing.
Aerosol tubing -
A piece of tubing used to deliver inhaled medicine (breathing treatment) to
patients with tracheostomy or breathing tube.
Cannula - A hollow piece of tubing: inner cannula
refers to the inner tubing of a standard tracheostomy tube.
Coagulopathies - Refers to diseases
or conditions causing problems with clotting of blood, for example low platelet
count or patients taking blood thinners like aspirin or coumadin.
Decannulation - Process
of removing the tracheostomy tube and making sure the patient is breathing well
without it.
Extubation - Process
of removing a breathing tube (endotracheal tube) when the patient does not need
it any more.
Heat Moisture Exchanger (HME) - A humidifying filter that fits onto the end of
the trach tube and comes in several shapes and sizes; also known as: Thermal
Humidfying Filters, Swedish nose, Artificial nose, Filter, Thermovent T.
Hypercarbia - A
condition in which more than normal amounts of carbon dioxide in retained in a
patient’s blood due to inadequate breathing.
Laryngectomy - It is the removal of the larynx and separation
of the airway from the mouth and esophagus.
NPO feeding (PO feeding) – No Per Oral
NPO feeding (
Nebulizer bottle - A bottle used to
turn liquid (saline etc) or a liquid medication into smaller particles to be
delivered to a patient’s nose, throat or lungs via the nose, mouth or a
breathing tube.
Obturator - Provide
a smooth surface that guides the tracheostomy tube when it is being inserted.
Passy-Muir Speaking Valve – A one-way valve, which attaches to the outside opening of the
tracheostomy tube and allows air to pass into the tracheostomy, but not out
through it.
Secretions - Mucus.
Suction Equipment
Stopper (plug/cork) - A device used to obstruct air passage through a tracheostomy tube to allow a patient to breathe around the tube before the tracheostomy tube is removed (decannulated).
Stopper (plug/cork) - A device used to obstruct air passage through a tracheostomy tube to allow a patient to breathe around the tube before the tracheostomy tube is removed (decannulated).
Tracheostomy - An
opening surgically created through the neck into the trachea to allow direct
access to the breathing tube.
Tracheotomy - Refers to the incision into the trachea that forms a temporary or permanent opening, which is called a 'tracheostomy,' however; the terms are sometimes used interchangeably
Tracheotomy - Refers to the incision into the trachea that forms a temporary or permanent opening, which is called a 'tracheostomy,' however; the terms are sometimes used interchangeably





.jpg)


















No comments:
Post a Comment